Planting a rose garden can be a rewarding and enjoyable hobby, as roses are beautiful and fragrant plants that add color and interest to any garden. Roses symbolize love and courage. The right way to start your rose garden is to first decide which kind of rose bush you should plant based on your location. Here are a few recommended types:
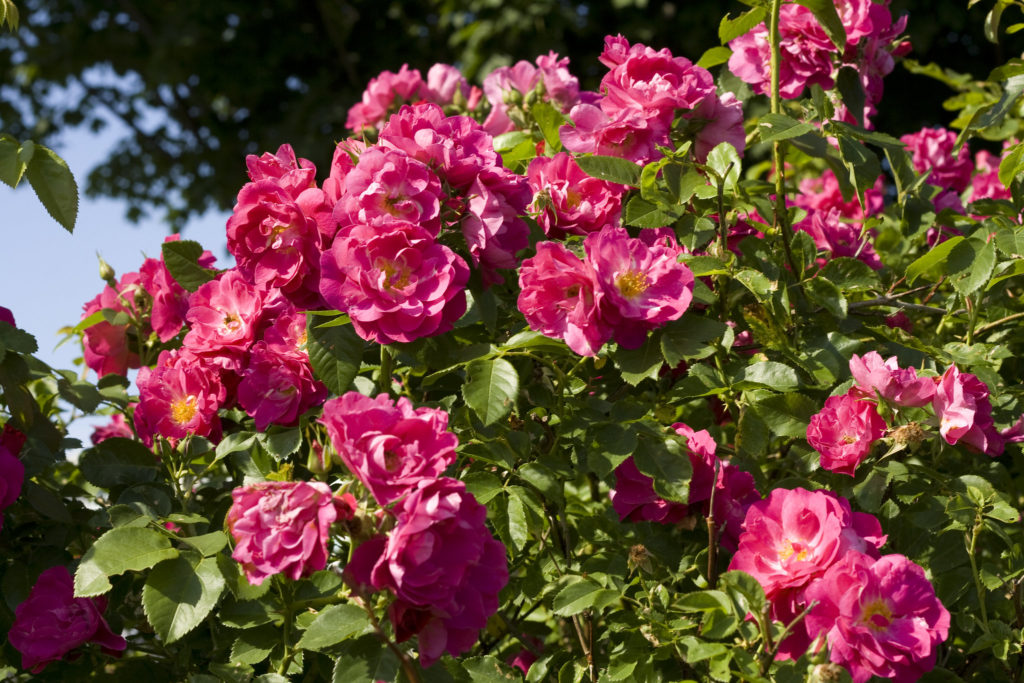

- Hybrid tea roses: Hybrid tea roses are popular for their large, showy blooms and sweet fragrance. They are long-stemmed roses that are perfect for cutting and can be grown in a wide range of climates.
- Floribunda roses: Floribunda roses are known for their abundant clusters of small to medium-sized flowers. They are typically more disease-resistant than hybrid tea roses and are well-suited for mass plantings or mixed borders.
- Grandiflora roses: Grandiflora roses are a cross between hybrid tea and floribunda roses, and they are known for their large, showy blooms and strong, upright growth habit. They are well-suited for use as a hedge or background plant.
- Climbing roses: Climbing roses are a great choice for adding vertical interest to your garden. They are well-suited for trellises, arbors, or other structures and can be grown in a wide range of climates.
- Old garden roses: Old garden roses, also known as heritage roses, are a group of roses that were popular in the past and include varieties such as Damask roses, Alba roses, and Centifolia roses. They are known for their fragrant blooms and old-fashioned charm.
Ultimately, the best roses for your garden will depend on your personal preferences and the growing conditions in your area. It’s always a good idea to do some research and choose varieties that are well-suited to your climate and soil type. Find rose suppliers on Garden Savvy or consult with them on what the best kind of rose you should be planting in your garden.
Rose Growing Guide
 Now that you’ve selected a rose variety, here is our in-depth guide on how to plant, grow, and care for a rose garden.
Now that you’ve selected a rose variety, here is our in-depth guide on how to plant, grow, and care for a rose garden.
It all starts with choosing the right location. Roses need at least six hours of direct sunlight per day and well-draining soil. Avoid planting them in areas that are prone to standing water or heavy shade. Next, you will need to prepare your soil by removing any weeds and adding organic matter such as compost or well-rotted manure to improve the soil structure and fertility. Here is more detail on how to prepare your soil:
- Test the pH of your soil: Roses prefer soil with a pH between 6.0 and 6.5, so it’s a good idea to test the pH of your soil to ensure it is in the proper range. You can purchase a soil pH testing kit from a supplier on Garden Savvy or a local garden center.
- Add organic matter: Adding organic matter such as compost or manure to your soil can help improve the soil structure and fertility. This is especially important for heavy clay soils, as organic matter can help improve drainage and aeration.
- Add lime: If your soil has a pH lower than 6.0, you may need to add lime to raise the pH. Lime can be purchased from a supplier on Garden Savvy or at a local garden center. Always follow package instructions on how to apply.
- Remove weeds and debris: Before planting your roses, remove any weeds and debris from the area where you will be planting. This will help prevent competition for resources and ensure that your roses have the best chance of establishing themselves.
When planting roses, dig a hole that is slightly larger than the root ball of the plant. Place the plant in the hole, making sure that the bud union (the point where the roots meet the canes) is level with the soil surface. Backfill the hole with soil, compost, and gently tamp down to remove any air pockets. Water the plant well to help it establish itself. Adding some mulch helps to conserve moisture and suppress weeds, so be sure to spread a layer of mulch around your roses after planting.
Rose Plant Care
 Water your roses regularly. Roses need regular watering to stay healthy and produce beautiful blooms. Water them deeply at least once a week, making sure to moisten the soil to a depth of at least 6 inches. Avoid getting water on the foliage, as this can encourage fungal diseases.
Water your roses regularly. Roses need regular watering to stay healthy and produce beautiful blooms. Water them deeply at least once a week, making sure to moisten the soil to a depth of at least 6 inches. Avoid getting water on the foliage, as this can encourage fungal diseases.
Fertilize your roses every six to eight weeks during the growing season with a balanced fertilize that contains nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium. Avoid using too much fertilizer, as it can encourage foliage growth at the expense of flowers.
Pruning is also critical to the health and prosperity of your rose bushes. Pruning helps to remove dead or damaged wood and encourages new growth. It’s best to prune roses in late winter or early spring, before new growth begins. Start by removing any dead or damaged canes and then prune the remaining canes back by about one-third.
Rose Pests and Disease Management

Protect your roses from pests and diseases. Keep an eye out for pests such as aphids, thrips, and Japanese beetles, and take steps to control them as needed. Roses are also prone to fungal diseases such as black spot and powdery mildew, so be sure to monitor for these and treat as needed. Here is more detail on how to handle these pests and diseases.
- Black spot: Black spot is a fungal disease that causes dark spots to appear on the leaves of rose plants. To treat black spot, remove and destroy infected leaves and spray the plant with a fungicide. Avoid overhead watering and improve air circulation around the plants to help prevent the disease.
- Powdery mildew: Powdery mildew is another fungal disease that causes a white, powdery coating to appear on the leaves and stems of rose plants. To treat powdery mildew, remove and destroy infected leaves and apply a fungicide. Avoid overcrowding plants and improve air circulation to help prevent the disease.
- Aphids: Aphids are small, sap-sucking insects that can damage rose plants by feeding on the leaves and stems. To control aphids, remove and destroy infested leaves and spray the plant with an insecticide. You can also attract natural predators such as ladybugs and lacewings to help control aphid populations.
- Thrips: Thrips are small, slender insects that feed on the foliage of rose plants, causing damage and discoloration. To control thrips, remove and destroy infested leaves and apply an insecticide. Avoid overcrowding plants and improve air circulation to help prevent thrips infestations.
- Japanese beetles: Japanese beetles are a common pest of roses, feeding on the leaves and flowers of the plant. To control Japanese beetles, remove and destroy any beetles you find on the plant and apply an insecticide. You can also use physical barriers such as netting to protect your roses from Japanese beetles.
By following these tips, you can successfully plant, grow, and care for a beautiful rose garden that will bring joy and beauty to your yard for years to come. If you want to plan out your rose garden first, try our garden planner Hortisketch. Or, join our gardening community and join a rose group to ask questions from your peers.